FLUNECY IN IT - GROUP PROJECT
Chapter 2: Learning about technology
For humans to learn about technology, we need to account how it works as well as learning and training ourselves in how it’s used. People within the technological society are able to use a tool such as a CD player and easily find the use of it simple. Most people do not need to refer to a user manual in order to figure out how to work this. Most of us know and can even guess what the controls do in order to play music. Human try things out and learn from our mistake and try again until the desired outcome occurs.
The Desktop
The desktop
When computer is turned on, the image that you see on display from the monitor is called the desktop. On a desktop, it usually displays icons, patterns, pictures etc, these are common background images. On the desktop, information is displayed along the side or top of the desktop by three different kinds of icons. These icons are;
Applications (programs): Internet Explorer
Folders (directories): small file folders
Files (documents): icon corresponding to the application such as Adobe Acrobat.
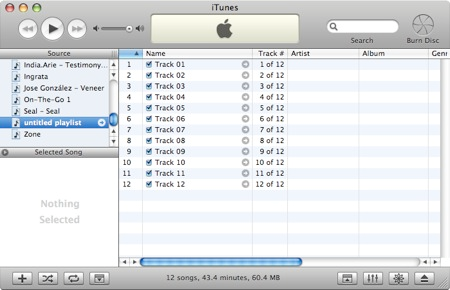
This is called a desktop because it implies a metaphor. A metaphor is an object/idea used as a concept for computation. To demonstrate how metaphors are applied, consider listing to music. For example when we play music from a CD to the computer, we are able to control the software that is provided using a Graphical User Interface (GUI). For example iTunes is a well-known music software to play music for an MAC operating system. However, standard music players on other operating systems are used and even if iTunes is not familiar, we are able to look and figure out how it works.
From the GUI, this allows us to use and figure out or guess how software works as the software is being shown from the GUI. From the example of iTunes we can easily work out what each of the buttons do. The red is close, yellow (minimize) and green (maximize) which are all common to Mac's. You can also see there are three plastic like buttons which are meaningful for us to use the software to play music and move between tracks. By theside of the buttons is a simple volume control bar to adjust the volume.
As we all know that when a button is pushed when you click the mouse, anyone who has played music from iTunes can easily control the iTunes GUI. The software designers have presented a metaphor that we all easily understand and would not need any instructions and therefore we apply what we have learnt by using the software without any instructions given.
This is the same for other computer software.
Software designers put in a lot of time making GUI software programs easy for us to use and figure out without any instructions.
Consistent Interfaces
As we all know, computers perform many tasks as show GUI's use many different metaphors. When GUI's are built, they are built with simple metaphors such as buttons for example. The digerati are a collection of people who are measured the 'elite' of Information Technology. Whenever they see an icon or metaphor, they know how it works. Because of this, it seems that they know what they are doing even though they haven't used the software before. We will do same as this.
From the example of iTunes, it contains many basic and standard metaphors which are found in other GUI's.
One of them is command buttons. Command buttons are used basically in most software's. The shapes of buttons are usually oval, rectangle or circle. On the button is a command which tells us what command that button will perform when it is clicked on. To invoke the command, we simply click on the button with the mouse. When know the button has been clicked because the GUI produces a different screen, or change in colour or window.
Another common metaphor used is a slider control. Within iTunes are slider control is used to adjust the volume. Other forms of slider controls used are scroll bars which are located either at the bottom or right of a window. When information cannot fit onto one page either vertically or horizontally (this is mainly because the window as been minimised), a scroll appears to adjust the window and scroll across or down the page to see more of the page.
Beginning users should come to grips quickly and become familiar with them. Computer software's have many functions/operations which are similar to others and so software designers use them consistently as user's are always using them and so it takes advantage of our knowledge and experience in using them. More advanced users will look out for similar metaphors and when a new one occurs they use it and gain experience from it.
Anatomy of an Interface
Within a window where users interact by typing or clicking, there are menus. A menu is a list of functions that the software can do. Menus are listed across the top of the window, which is also known as the menu bar. A menu holds all operations which that software can perform.
Menu Operation
Menus which are listed across the top of the window and are in the menu bar are also called 'pull-down' or 'drop-down' menus. In order for the menu to drop or pull down, it will require a mouse click which will show other operations.
Reading a Menu
Menus don't only show what operations are provided but also if they are available at that time or even shortcuts but the name of the operation. For example the 'copy' or 'paste' function will not be available if nothing has been copied. The shortcut for 'copy' would be Ctrl C and paste would be Ctrl V. These shortcuts are shown by the side of the operation. If the operation is unavailable it will be shown in a light grey colour, compared to when an operation is available it is in black.
Chapter Selection
Top of Page


