 java.awt.Component
java.awt.Component
 java.awt.Container
java.awt.Container
 java.awt.Panel
java.awt.Panel
 java.applet.Applet
java.applet.Applet
 org.jcsp.awt.ActiveApplet
org.jcsp.awt.ActiveApplet
|
CSP for Java (JCSP) 1.1-rc4 |
||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
java.lang.Objectjava.awt.Component
java.awt.Container
java.awt.Panel
java.applet.Applet
org.jcsp.awt.ActiveApplet
public class ActiveApplet
java.applet.Applet
with a channel interface, specialising in the operation
of CSProcess networks as applets.
Shortcut to the Constructor and Method Summaries.
Applet to simplify
the management of an associated CSProcess. There are three
areas of provision:
Panel;
Parallel) process from the main thread of control.
We cannot do this from the applet init or start methods since
the browser would freeze until the process network terminated. Instead, the process
network must be started asynchronously with the applet thread. This can be achieved
by using a ProcessManager.
We could do this by directly extending the Applet class and
overriding its start, stop and destroy methods suitably -
however, the necessary logic has already been built into this class. All the user
needs to do is override the init method to contruct the desired
CSProcess and register it with this ActiveApplet
(by means of the setProcess method).
For example:
import org.jcsp.awt.*;
public class Flasher extends ActiveApplet {
public void init () {
setProcess (new FlasherNetwork (500, this));
}
}
In the above, FlasherNetwork is the CSProcess that will be run
by the ActiveApplet. The 500 parameter defines the period
(in milliseconds) of its flashing and should really
be a parameter of the applet itself.
The reason for passing the reference to this into the FlasherNetwork
process is explained in the description of its implementation
in the next section.
When the HTML browser invokes start for the first
time, the CSProcess (registered by the setProcess
method) will be set running in its own thread of control. As the browser subsequently
invokes stop and start methods, events will be posted to channels
which may be optionally registered with the Applet.
When the browser invokes destroy, an event will be posted to the optionally registered channel. If this is not present or does not cause network termination the process network will be forcefully destroyed.
| Use of this ActiveApplet class is recommended only for browsers on systems that have installed Sun's Java Plug-in. |
This has the robust behaviour of invoking a destroy immediately following a stop whenever we leave a web page containing a Plug-in controlled applet. It re-launches the applet from scratch whenever we return. Whilst this removes the option of allowing applets continued execution during visits to other pages (but see the cheat), it does relieve various deadlock problems that may otherwise strike our browser.
Note: to use the Java Plug-in, HTML pages containing applets must be transformed using the Java Plug-in HTML Converter. This renders the HTML somewhat more complex than it was before conversion, but the results are worthwhile. A browser visiting such a page without the Plug-in installed is invited to install it - a link is offered to make this easy.
The methods setStopStartChannel and
setDestroyChannels let us connect special channels
to the ActveApplet process:
ActiveApplet.STOP
(respectively ActiveApplet.START)
will be written to this channel whenever the browser invokes a stop
(respectively start) method. As before, the first invocation
of start just starts the running of the associated process
(i.e. ActiveApplet.START messages are only sent on second and
subsequent starts).
This replaces the default start and stop mechanisms
described earlier.
If a pair of destroy/destroyAck channels have been set,
an ActiveApplet.DESTROY will be written to the destroy
channel when the browser invokes its destroy method.
The browser will wait for up to 10 seconds (by default)
for the applet process to respond with a message on destroyAck, before
proceeding to execute the default destroy mechanisms.
The timeout period can be specified (or disabled)
when the channels are set.
These channels should be set up either as an explicit part of the init method (and passed to the user process as a constructor or mutator parameter) or by the user process constructor itself (to which this ActveApplet would have had to have been passed). It is important that these channels are in place before the user process starts running (otherwise the default mechanism may be triggered if the user quits the ActveApplet web page or the browser too quickly).
It is crucial, of course, that these communications are accepted by the user process associated with the ActveApplet. Using a channel configured with an overwriting buffer (of capacity one) will ensure this. Note that this overwriting cannot cause the loss of any significant information to the user process.
The stop/start and destroy operations are implemented via separately set channels so that the designer may make separate decisions on whether to use each of them.
Freezing a process network (e.g. in response to
a STOP is usually easy to arrange - just pinch the data-flow at a crucial
point to achieve a temporary deadlock. When the START message arrives,
just let go.
Note: if the Java Plug-in is not being used, it is strongly recommended to set and operate this stopStart channel (rather than rely on the default suspend operations).
Note: if the Java Plug-in is being used, user-defined behaviour for the stop/start operations are not needed. Any stop is quickly followed by a destroy (for which the default ActveApplet response will release any locked resource). Second invocations of start never take place.
The destroy/destroyAck channels enable the process network to tidy up any created resources (e.g. to make invisible and dispose of any widgets spawned off the web page) before termination. Correctly terminating a process network (e.g. in response to a destroy) is usually harder to arrange safely - so it may be better to leave this to the default mechanism (which will follow the destroyAck signal). However, secure CSP algorithms, at least for 1-1 channels, are known (e.g. the graceful termination protocol) and support for this may be provided in later versions of this library.
Note: if the destroy/destroyAck channels have been set, the default suspend mechanism (if not already overridden by setting a stopStart channel) will be suppressed. This is because the browser invokes the stop method immediately before invoking the destroy. If we did not do this, the suspended network would not be able to respond to the destroy channel.
java.applet.Applet
which extends a java.awt.Panel. Most activeApplets
will just use this panel as a container for other active GUI processes that
form part of their ActiveApplet network. However, if there is a need for run-time
configuration of the underlying panel and/or reaction to GUI events occurring on the
panel, the ActveApplet can itself be used as a process in that network.
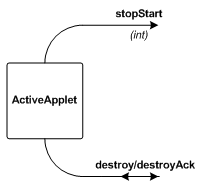
Fot this case, an ActveApplet has a channel interface (which, together with
the browser control channels, extends that offered by
an ActivePanel):
All channels are optional. The configure channel is connected by invoking
the setConfigureChannel method.
Event channels can be added to notify the occurrence of any type of Event
the component generates (by calling the appropriate
addXXXEventChannel method before the process is run).
Messages can be sent down the configure channel at any time to configure
the component. See the table below for details.
All channels are managed by independent internal handler processes. It is, therefore, safe for a serial application process both to service an event channel and configure the component -- no deadlock can occur.
IMPORTANT: it is essential that event channels from this process are always serviced -- otherwise the Java Event Thread will be blocked and the GUI will stop responding. A simple way to guarantee this is to use channels configured with overwriting buffers. For example:
final One2OneChannel myMouseEvent =
Channel.one2one (new OverWriteOldestBuffer (n));
activeApplet.addMouseEventChannel (myMouseEvent);
This will ensure that the Java Event Thread will never be blocked.
Slow or inattentive readers may miss rapidly generated events, but
the n most recent events will always be available.
| Input Channels | ||
|---|---|---|
| destroyAck | int | See the setDestroyChannels methods. |
| configure | ActiveApplet.Configure |
Invoke the user-defined Configure.configure method on the applet. |
| Output Channels | ||
| stopStart | int | See the setStopStartChannel method. |
| destroy | int | See the setDestroyChannels methods. |
| containerEvent | ContainerEvent | See the addContainerEventChannel method. |
| componentEvent | ComponentEvent | See the addComponentEventChannel method. |
| focusEvent | FocusEvent | See the addFocusEventChannel method. |
| keyEvent | KeyEvent | See the addKeyEventChannel method. |
| mouseEvent | MouseEvent | See the addMouseEventChannel method. |
| mouseMotionEvent | MouseEvent | See the addMouseMotionEventChannel method. |
Here is the code to set up this process:
import org.jcsp.lang.*;
import org.jcsp.awt.*;
public class FlasherNetwork implements CSProcess {
final private long period;
final private ActiveApplet activeApplet;
public FlasherNetwork (final long period,
final ActiveApplet activeApplet) {
this.period = period;
this.activeApplet = activeApplet;
}
public void run () {
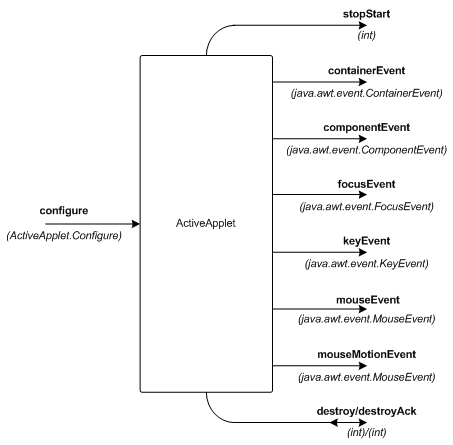
final One2OneChannel mouseEvent = Channel.one2one ();
final One2OneChannel appletConfigure = Channel.one2one ();
activeApplet.addMouseEventChannel (mouseEvent.out ());
activeApplet.setConfigureChannel (appletConfigure.in ());
new Parallel (
new CSProcess[] {
activeApplet,
new FlasherControl (period, mouseEvent.in (), appletConfigure.out ())
}
).run ();
}
}
FlasherControl demonstrates three basic JCSP techniques:
ALTing between guards (a channel
communication and a timeout);
ALTing with pre-conditions
(the mouse must be present in the applet for the flashing - controlled
by the timeout - to take place);
ActiveApplet.Configure).
import org.jcsp.lang.*;
import org.jcsp.awt.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
public class FlasherControl implements CSProcess {
final private long period;
final private AltingChannelInput mouseEvent;
final private ChannelOutput appletConfigure;
public FlasherControl (final long period,
final AltingChannelInput mouseEvent,
final ChannelOutput appletConfigure) {
this.period = period;
this.mouseEvent = mouseEvent;
this.appletConfigure = appletConfigure;
}
private class AppletColour implements ActiveApplet.Configure {
private Color colour = Color.lightGray;
public void setColour (Color colour) {
this.colour = colour;
}
public void configure (java.applet.Applet applet) {
applet.setBackground (colour);
}
}
public void run () {
final Random random = new Random ();
final CSTimer tim = new CSTimer ();
final Alternative alt = new Alternative (new Guard[] {mouseEvent, tim});
final boolean[] preCondition = {true, false};
final int MOUSE = 0;
final int TIMER = 1;
final AppletColour[] appletColour = {new AppletColour (), new AppletColour ()};
final AppletColour panelBlack = new AppletColour ();
panelBlack.setColour (Color.black);
appletConfigure.write (panelBlack);
int index = 0;
AppletColour appletCol = appletColour[index];
appletCol.setColour (new Color (random.nextInt ()));
long timeout = tim.read ();
boolean mousePresent = false;
boolean running = true;
while (running) {
switch (alt.priSelect (preCondition)) {
case MOUSE:
switch (((MouseEvent) mouseEvent.read ()).getID ()) {
case MouseEvent.MOUSE_ENTERED:
if (! mousePresent) {
mousePresent = true;
timeout = tim.read () + period;
tim.setAlarm (timeout);
appletConfigure.write (appletCol);
preCondition[TIMER] = true;
}
break;
case MouseEvent.MOUSE_EXITED:
if (mousePresent) {
mousePresent = false;
appletConfigure.write (panelBlack);
preCondition[TIMER] = false;
}
break;
}
break;
case TIMER:
timeout += period;
tim.setAlarm (timeout);
index = 1 - index;
appletCol = appletColour[index];
appletCol.setColour (new Color (random.nextInt ()));
appletConfigure.write (appletCol);
break;
}
}
}
}
All methods getAppletXXX have the same form, where XXX is one of Java's primitive types (int, boolean, byte, short, long, float and double). Each returns an XXX value, parsed from the applet parameter named in the method's first parameter. A standby value must be supplied in case the named applet parameter does not exist or parse correctly. The number returning methods must supply min and max values against which the applet supplied value will be checked - values below min being truncated to min and values above max to max.
For example, Flasher should really acquire its period value as an applet parameter:
import org.jcsp.lang.*;
import org.jcsp.awt.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class Flasher extends ActiveApplet {
public static final int minPeriod = 300; // milliseconds
public static final int maxPeriod = 1000; // milliseconds
public static final int defaultPeriod = 500; // milliseconds
public void init () {
final int period =
getAppletInt ("period", minPeriod, maxPeriod, defaultPeriod);
setProcess (new FlasherNetwork (period, this));
}
}
Now, if no applet parameter "period" is present, the defaultPeriod
is chosen. Same if the parameter was present but doesn't parse. Otherwise,
values below minPeriod are rounded up to minPeriod,
values above maxPeriod are rounded down to maxPeriod
and good values are just accepted.
Applet,
Panel,
ContainerEvent,
ComponentEvent,
FocusEvent,
KeyEvent,
MouseEvent,
OverWriteOldestBuffer,
Serialized Form| Nested Class Summary | |
|---|---|
static interface |
ActiveApplet.Configure
This enables general configuration of this component. |
| Nested classes/interfaces inherited from class java.applet.Applet |
|---|
Applet.AccessibleApplet |
| Nested classes/interfaces inherited from class java.awt.Panel |
|---|
Panel.AccessibleAWTPanel |
| Nested classes/interfaces inherited from class java.awt.Container |
|---|
Container.AccessibleAWTContainer |
| Nested classes/interfaces inherited from class java.awt.Component |
|---|
Component.AccessibleAWTComponent, Component.BltBufferStrategy, Component.FlipBufferStrategy |
| Field Summary | |
|---|---|
static int |
DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_ACK
This is the default time (in milliseconds) that the browser will wait for the applet process to acknowledge (on destroyAck) a DESTROY message (sent down destroy). |
static int |
DESTROY
This value is sent down a destroy channel
when the browser invokes a destroy -
see the user-defined destroy response. |
static int |
START
This value is sent down a stopStart channel
on second and subsequent browser invocations of start -
see the user-defined stop/start response. |
static int |
STOP
This value is sent down a stopStart channel
when the browser invokes a stop -
see the user-defined stop/start response. |
| Fields inherited from class java.awt.Component |
|---|
BOTTOM_ALIGNMENT, CENTER_ALIGNMENT, LEFT_ALIGNMENT, RIGHT_ALIGNMENT, TOP_ALIGNMENT |
| Fields inherited from interface java.awt.image.ImageObserver |
|---|
ABORT, ALLBITS, ERROR, FRAMEBITS, HEIGHT, PROPERTIES, SOMEBITS, WIDTH |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
ActiveApplet()
|
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
void |
addComponentEventChannel(ChannelOutput componentEvent)
Add a new channel to this component that will be used to notify that a ComponentEvent has occurred. |
void |
addContainerEventChannel(ChannelOutput containerEvent)
Add a new channel to this component that will be used to notify that a ContainerEvent has occurred. |
void |
addFocusEventChannel(ChannelOutput focusEvent)
Add a new channel to this component that will be used to notify that a FocusEvent has occurred. |
void |
addKeyEventChannel(ChannelOutput keyEvent)
Add a new channel to this component that will be used to notify that a KeyEvent has occurred. |
void |
addMouseEventChannel(ChannelOutput mouseEvent)
Add a new channel to this component that will be used to notify that a MouseEvent has occurred. |
void |
addMouseMotionEventChannel(ChannelOutput mouseMotionEvent)
Add a new channel to this component that will be used to notify that a MouseMotionEvent has occurred. |
void |
destroy()
Called by the browser when the ActiveApplet needs to be destroyed. |
boolean |
getAppletBoolean(String parameter,
boolean standby)
This looks for the named parameter in the HTML applet source code and attempts to parse it into a boolean. |
byte |
getAppletByte(String parameter,
byte min,
byte max,
byte standby)
This looks for the named parameter in the HTML applet source code and attempts to parse it into a byte. |
double |
getAppletDouble(String parameter,
double min,
double max,
double standby)
This looks for the named parameter in the HTML applet source code and attempts to parse it into a double. |
float |
getAppletFloat(String parameter,
float min,
float max,
float standby)
This looks for the named parameter in the HTML applet source code and attempts to parse it into a float. |
int |
getAppletInt(String parameter,
int min,
int max,
int standby)
This looks for the named parameter in the HTML applet source code and attempts to parse it into an int. |
long |
getAppletLong(String parameter,
long min,
long max,
long standby)
This looks for the named parameter in the HTML applet source code and attempts to parse it into a long. |
short |
getAppletShort(String parameter,
short min,
short max,
short standby)
This looks for the named parameter in the HTML applet source code and attempts to parse it into a short. |
void |
run()
The main body of this process. |
void |
setConfigureChannel(ChannelInput configure)
Sets the configuration channel for this ActiveApplet. |
void |
setDestroyChannels(ChannelOutputInt destroy,
AltingChannelInputInt destroyAck)
This sets destroy/destroyAck channels to allow a user-defined destroy response. |
void |
setDestroyChannels(ChannelOutputInt destroy,
AltingChannelInputInt destroyAck,
int timeoutAck)
This sets destroy/destroyAck channels to allow a user-defined destroy response. |
void |
setProcess(CSProcess process)
This must be called during the init() method for this ActiveApplet. |
void |
setStopStartChannel(ChannelOutputInt stopStart)
This sets a stopStart channel to allow a user-defined stop/start response. |
void |
start()
Called by the browser when the ActiveApplet is first started and each time its web page is revisited. |
void |
stop()
Called by the browser when the web page containing this ActiveApplet is replaced by another page or just before this ActiveApplet is to be destroyed. |
| Methods inherited from class java.applet.Applet |
|---|
getAccessibleContext, getAppletContext, getAppletInfo, getAudioClip, getAudioClip, getCodeBase, getDocumentBase, getImage, getImage, getLocale, getParameter, getParameterInfo, init, isActive, newAudioClip, play, play, resize, resize, setStub, showStatus |
| Methods inherited from class java.awt.Panel |
|---|
addNotify |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait |
| Field Detail |
|---|
public static final int STOP
stopStart channel
when the browser invokes a stop -
see the user-defined stop/start response.
public static final int START
stopStart channel
on second and subsequent browser invocations of start -
see the user-defined stop/start response.
public static final int DESTROY
destroy channel
when the browser invokes a destroy -
see the user-defined destroy response.
public static final int DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_ACK
| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public ActiveApplet()
| Method Detail |
|---|
public void setProcess(CSProcess process)
process - the process defining the applet behaviour.public void setStopStartChannel(ChannelOutputInt stopStart)
stopStart - the channel controlling the stop/start behaviour of the applet.
public void setDestroyChannels(ChannelOutputInt destroy,
AltingChannelInputInt destroyAck)
default timeout delay (10000 milliseconds)
for the applet process to acknowledge the destroy signal is set.
destroy - the channel to which a DESTROY will be written.destroyAck - the acknowledgement channel associated with destroy.
public void setDestroyChannels(ChannelOutputInt destroy,
AltingChannelInputInt destroyAck,
int timeoutAck)
destroy - the channel to which a DESTROY will be written.destroyAck - the acknowledgement channel associated with destroy.timeoutAck - the timeout (in milliseconds) allowed for the acknowledgement
- if negative, no timeout will be set.public void start()
start in class Appletpublic void stop()
stop in class Appletpublic void destroy()
destroy in class Applet
public int getAppletInt(String parameter,
int min,
int max,
int standby)
parameter - the applet parameter name.min - the minimum acceptable parameter value.max - the maximum acceptable parameter value.standby - the value to retun in case the applet parameter is bad.
public boolean getAppletBoolean(String parameter,
boolean standby)
parameter - the applet parameter name.standby - the value to retun in case the applet parameter is bad.
public byte getAppletByte(String parameter,
byte min,
byte max,
byte standby)
parameter - the applet parameter name.min - the minimum acceptable parameter value.max - the maximum acceptable parameter value.standby - the value to retun in case the applet parameter is bad.
public short getAppletShort(String parameter,
short min,
short max,
short standby)
parameter - the applet parameter name.min - the minimum acceptable parameter value.max - the maximum acceptable parameter value.standby - the value to retun in case the applet parameter is bad.
public long getAppletLong(String parameter,
long min,
long max,
long standby)
parameter - the applet parameter name.min - the minimum acceptable parameter value.max - the maximum acceptable parameter value.standby - the value to retun in case the applet parameter is bad.
public float getAppletFloat(String parameter,
float min,
float max,
float standby)
parameter - the applet parameter name.min - the minimum acceptable parameter value.max - the maximum acceptable parameter value.standby - the value to retun in case the applet parameter is bad.
public double getAppletDouble(String parameter,
double min,
double max,
double standby)
parameter - the applet parameter name.min - the minimum acceptable parameter value.max - the maximum acceptable parameter value.standby - the value to retun in case the applet parameter is bad.
public void setConfigureChannel(ChannelInput configure)
configure - the channel for configuration events.
If the channel passed is null, no action will be taken.public void addContainerEventChannel(ChannelOutput containerEvent)
NOTE: This method must be called before this process is run.
containerEvent - the channel down which to send ContainerEvents.public void addComponentEventChannel(ChannelOutput componentEvent)
NOTE: This method must be called before this process is run.
componentEvent - the channel down which to send ComponentEvents.public void addFocusEventChannel(ChannelOutput focusEvent)
NOTE: This method must be called before this process is run.
focusEvent - the channel down which to send FocusEvents.public void addKeyEventChannel(ChannelOutput keyEvent)
NOTE: This method must be called before this process is run.
keyEvent - the channel down which to send KeyEvents.public void addMouseEventChannel(ChannelOutput mouseEvent)
NOTE: This method must be called before this process is run.
mouseEvent - the channel down which to send MouseEvents.public void addMouseMotionEventChannel(ChannelOutput mouseMotionEvent)
NOTE: This method must be called before this process is run.
mouseMotionEvent - the channel down which to send MouseMotionEvents.public void run()
run in interface CSProcess
|
CSP for Java (JCSP) 1.1-rc4 |
||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||